Notes from Microeconomics 101
Table of Contents
1. Economic Systems
Economic resources: Things that are inputs to production of goods and services. There are Four economic resources or Four factors of production: land, labor, capital, and technology. Technology is sometimes referred to as entrepreneurship.
Land: Natural resources that are used in the production of goods and services. Some examples of land are lumber, raw materials, fish, soil, minerals, and energy resources.
Labor: Work effort used in the production of goods and services. Some examples are the number of workers and number of hours worked.
Capital: Physical goods that are produced and used to produce other goods. Examples of capital would be machinery, technology, and tools such as computers; hammers; factories; robots; trucks, and trains used to transport goods; and other equipment employed in the production of a good or service.
Technology (sometimes called entrepreneurship): The ability to combine the other productive resources into goods and services.
Not all costs are monetary costs. Opportunity costs are usually expressed in terms of how much of another good, service, or activity must be given up in order to pursue or produce another activity or good.
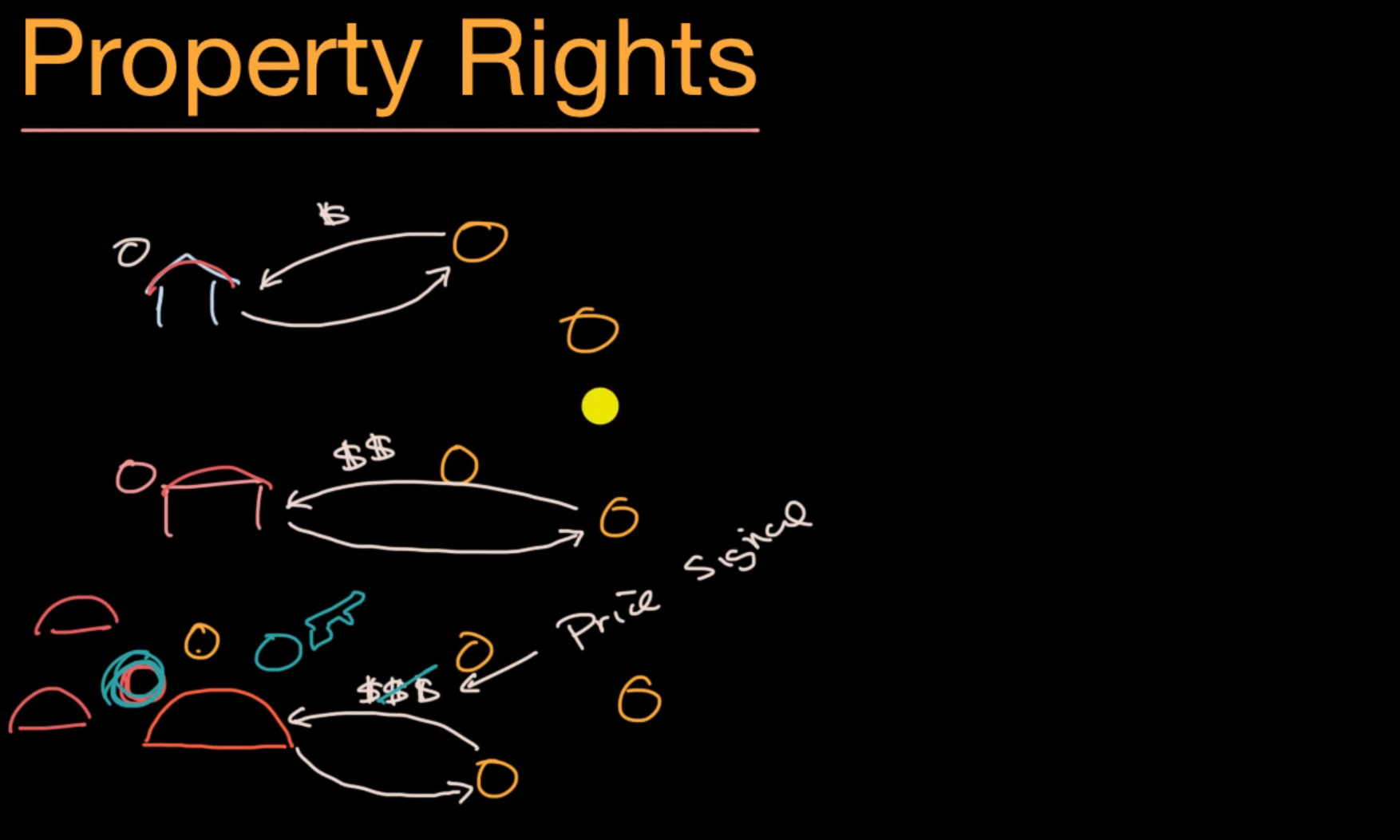
Property Right: an idea that is crucial for proper functioning of market based economy. Everyone agrees on who own what and what cant they do with that property.
Market gives price signal, based on demand. allocate resources efficiently based on demand and supply
Where there’s functioning property rights, the price signal maybe broken down - A market failure. The house analogy
Command economy has a major incentive problem. Little incentive to innovate, invest, build more
What is a market? (broad definition) - forms when multiple parties exchange things of value.
Market: A place where buyers and sellers meet to engage in mutually beneficial, voluntary exchanges of goods, services, or productive resources
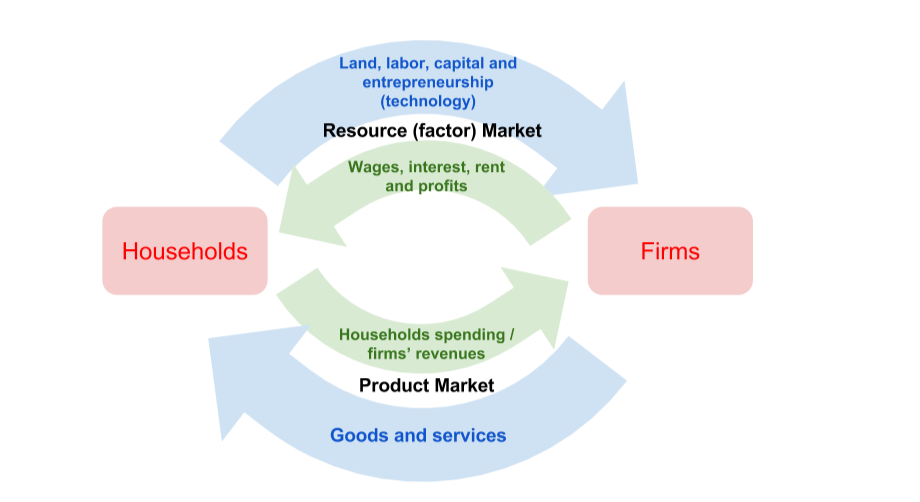
Households: The owners of resources—supplied to firms in the resource market—and the buyers of goods and services—demanded from firms in the product market
Firms: Business entities that demand land, labor, and capital from households in the resource market and produce goods and services, which they supply to households in the product market
Wages: The payment firms make to households in exchange for their labor
Rent: The payment firms make to households in exchange for land
Interest: The payment firms make to households in exchange for capital
Capitalism is based on the idea that markets are the most efficient way to allocate resources because they respond dynamically to supply, demand, and price signals.
What it means to “own” something in the notion of property rights?
- Exclusive: exclusive to the right owner to benefit of the thing
- Enforceable: by the rule of law
- Transferrable
The circular flow model illustrates how a market economy works. In the model, households and firms engage in mutually beneficial exchanges of resources and products in the market.