Notes from Finance & Capital Markets 101
Table of Contents
1. Interest and debt
1.1 Compound interest basics
Compound interest: Interest that gets applied on principal, that gets additive
The rule of 72 for compound interest: How long it takes to double money? (Approximate) (When compounding over set period of time, not continous)
Mutual funds are compunded too, as returns are invested into the sum
The rule is more accurate for lower interest rates than higher ones
The Rule of 69.3 is a more accurate formula for higher interest rate
1.2 Credit cards and loans
APR - Annual Percentage Rate
The rate is compounded on daily basis on what is owed. So, the compounded amount is exponential.
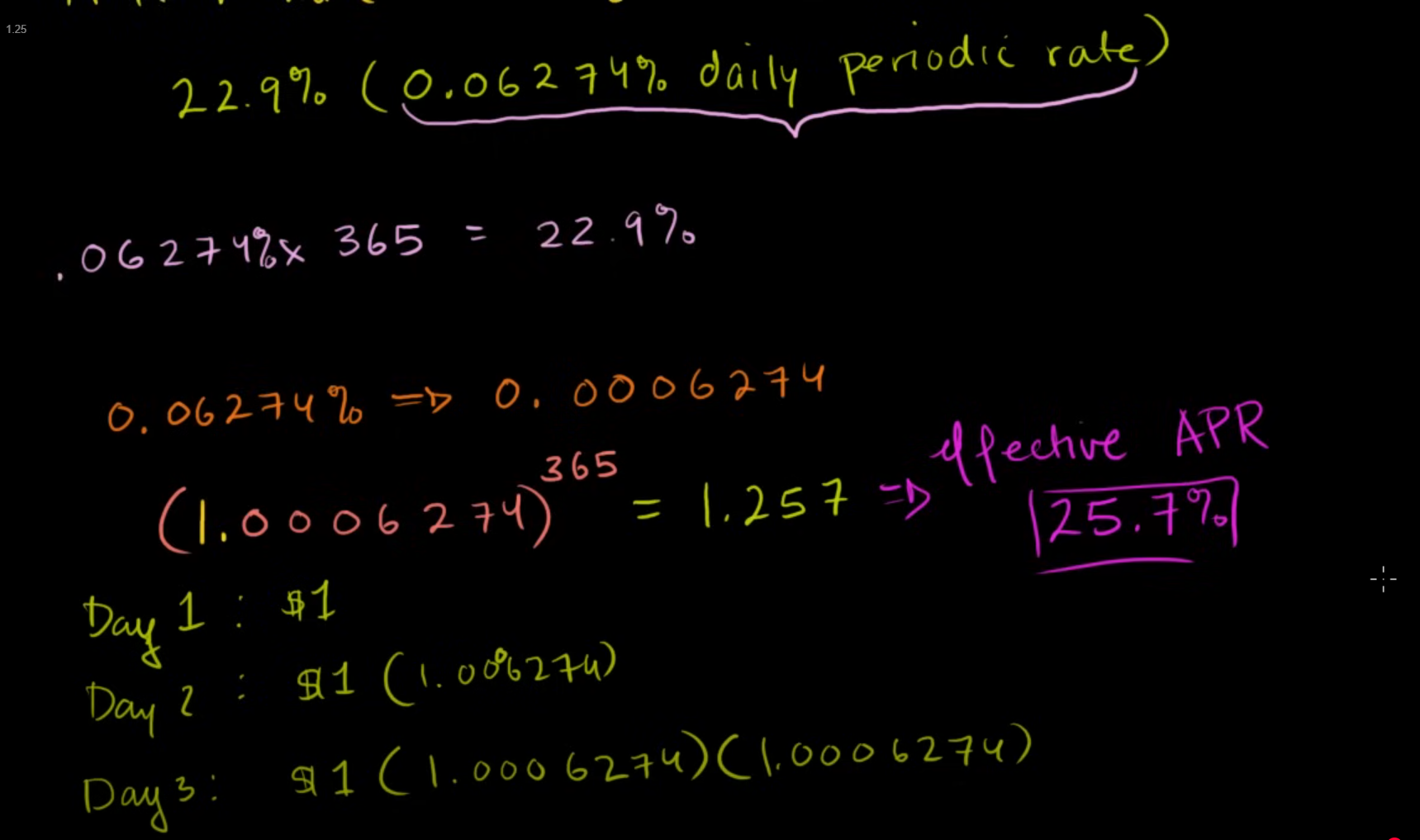
Lesson: Pay off your credit card debt as soon as possible. Do not carry balance.
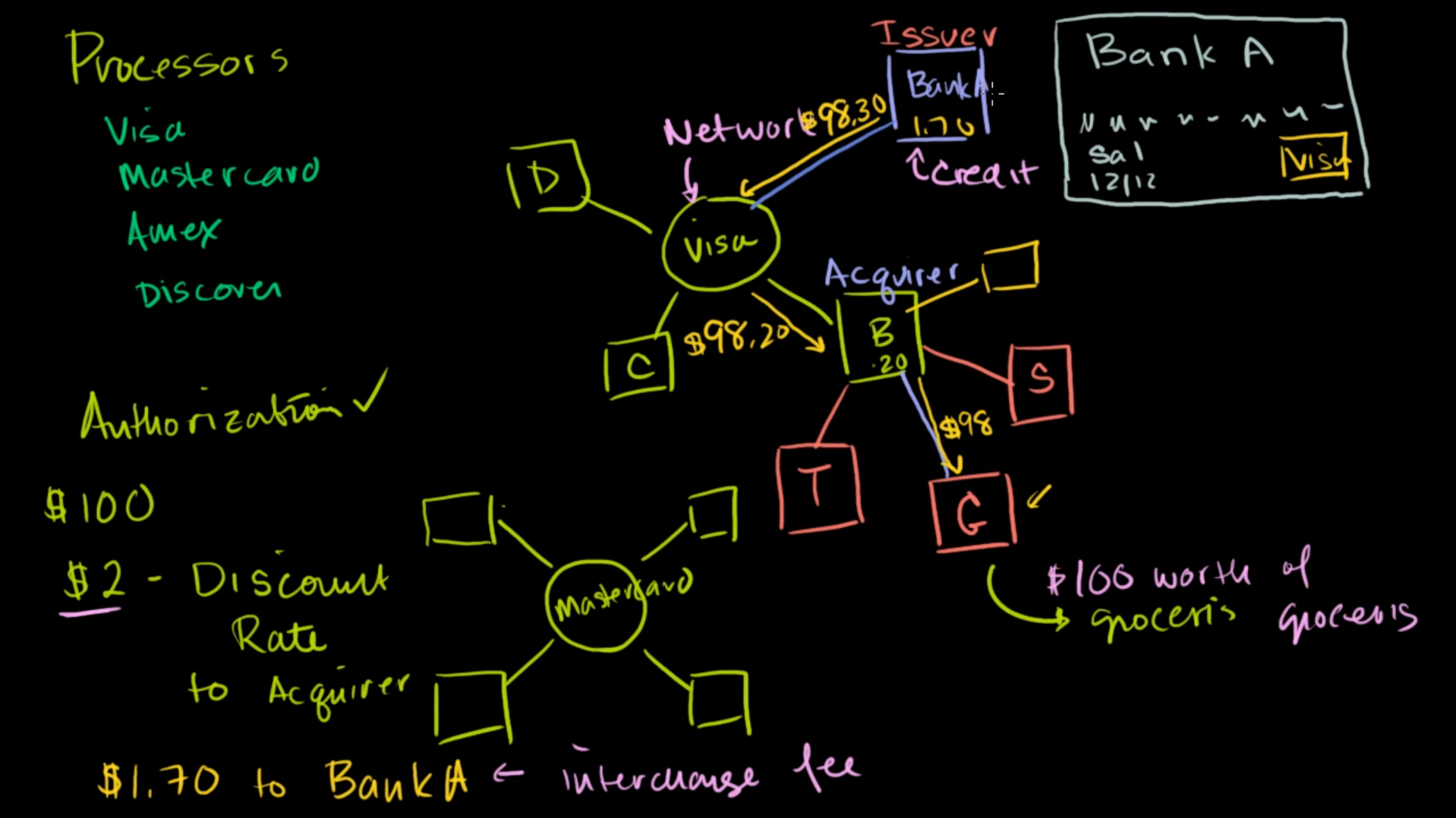
Institutional roles in issuing and processing credit cards
- Issuer - Bank that issues the card to the end user. If I am using HDFC Infinia, HDFC is the issuer.
- Processor - The networks the manages the settlement architecture. Visa, Mastercard, Amex etc.
- Merchant Acquirer - Bank that acquires the card transactions. Handles The machine where I swipe my card. If I swipe on a HDFC bank machine, the acquirer here is HDFC bank. Acquiring in this context refers to the process of bringing a merchant into the card payment network so they can accept card transactions.
MDR - Merchant Discount Rate. Fee as a percentage of the transaction amount. That gets divided into the players facilitating the entire transaction and settlement flow
The issuer bank gets the largest share of the MDR. As they take the risk of default on the card.